1.0 Background
Harvest supplies pressure-reducing mattresses (static and dynamic) to the health and social care sector within the UK. The company is committed to ensuring that the equipment it manufactures is subjected to post-market clinical follow-up (PMCF). Audits undertaken within the care provision sectors have sought to establish how the equipment functions in the real-world setting compared to laboratory/on-site testing. This document provides results and findings from audits undertaken between August and December 2022 in the Care Home Sector where the Balmoral Active Mattress is in use and has been compiled by an Independent Nurse Advisor / Educator on behalf of Harvest Health Care.
2.0 Findings
Data is provided for 82 residents in 11 independent care homes, however, it should be noted that not all data elements are available for all 82 residents due to the complexities of collecting audit data within the care home environment.
2.1 Age, Waterlow Score, and Weight
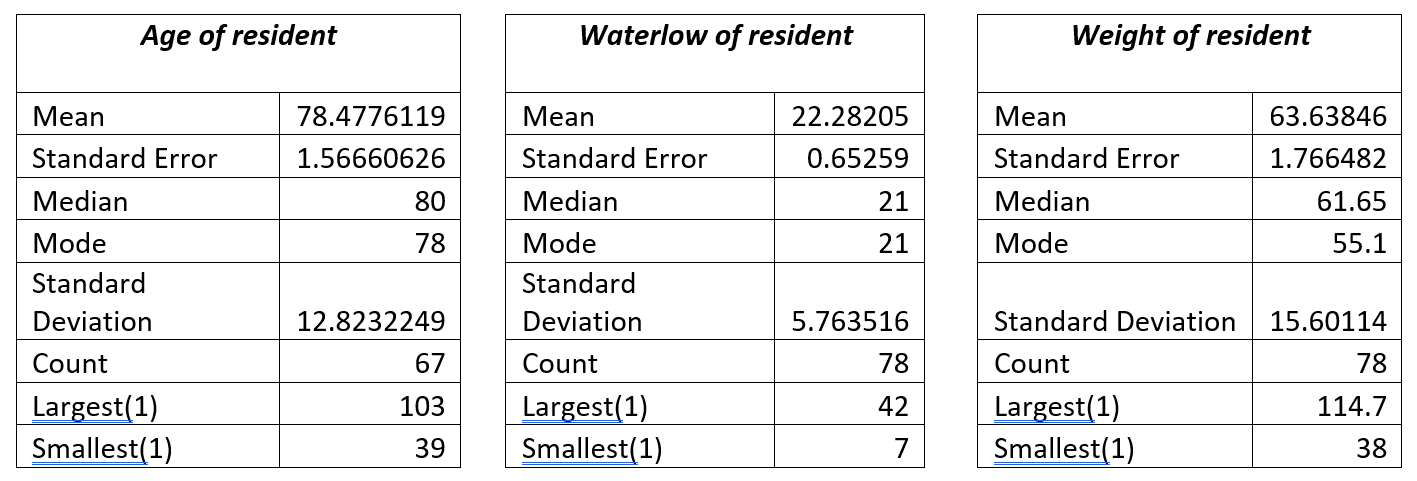
The age of the resident was available for 67 of the residents for whom audit data was available. The average age of residents nursed on the Harvest Balmoral mattress was 78 years, with the oldest resident at 103 years and the youngest resident was 39 years old. Waterlow scores for those who were managed on the Balmoral mattress ranged from WS 7 (not at risk) to WS42 (Very High Risk), with the average Waterlow score being 21 (Very High Risk). For the Waterlow data set, data was available for 78 of the 82 residents included in the audits. Weight ranges of those using the Balmoral mattress ranged from 38kg to 114.7 kg with an average weight of 63.3kg. Those with a weight of 38kg would usually be deemed to be extremely frail, and those with a weight of > 100kg in such an elderly population are likely to have high BMI and are most likely to be overweight or obese.
Figure 1 – Descriptive statistics for Age, Waterlow and Weight
2.2 Resident Mobility and Comorbidities
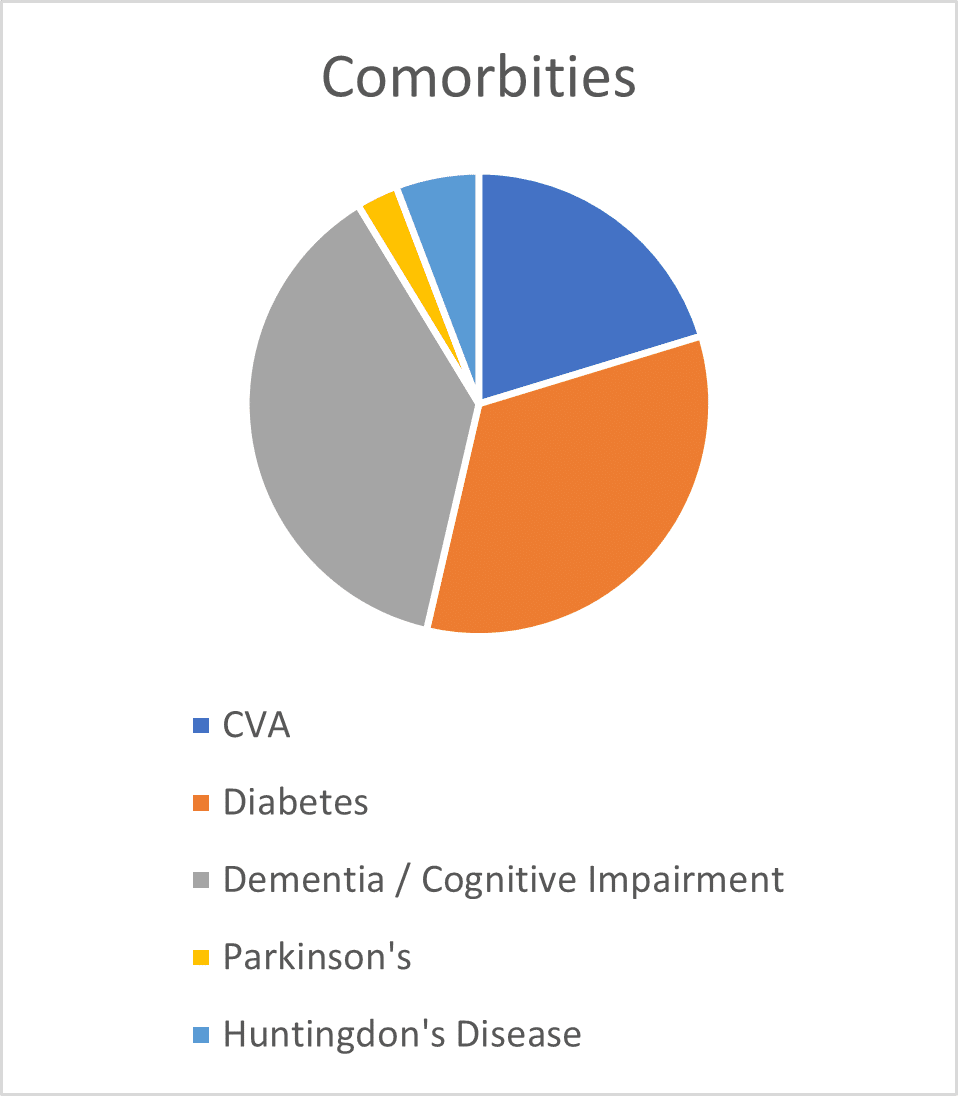
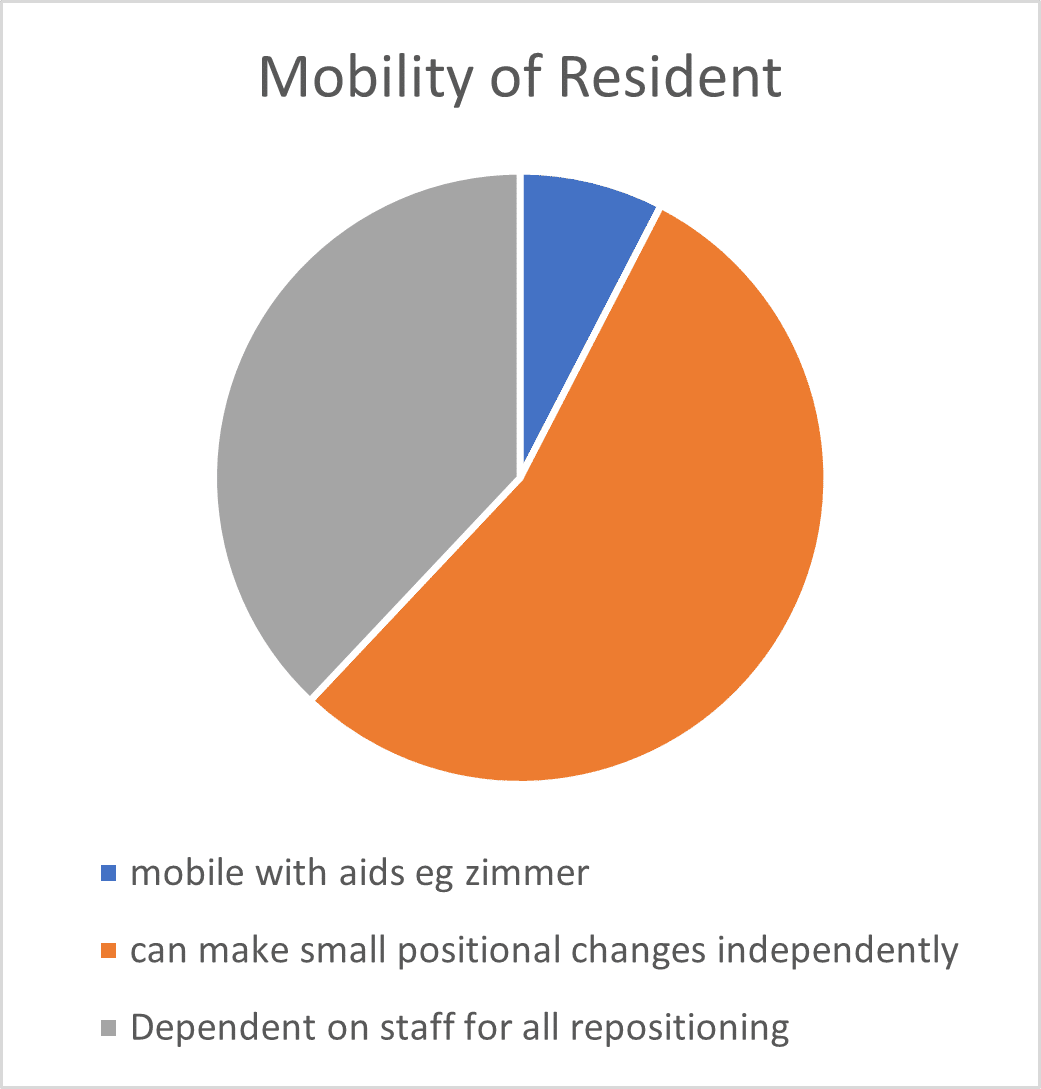
The audits undertaken by the independent clinical advisor also reviewed the mobility levels and comorbidities for each resident who was using the Harvest Balmoral. Findings are shown in Figures 1 and 2. Figure 1 shows that 92% of residents who were nursed on the Balmoral mattress had either poor mobility (required hoist or wheelchair, but were able to make some independent movements in bed) or were completely immobile (reliant on staff for all repositioning), with the remaining 8% able to mobilise with some assistance. The most common comorbidities (Figure 2) for those residents who were nursed on the Balmoral mattress, included (a) a history of Cerebral Vascular Accident (CVA 20%), (b) Dementia and/ or cognitive impairment (38%) and (c) Diabetes (33%).
Fig 1 Fig 2
2.3 Development of Pressure Ulcers
In total, during the audit period there were 8 residents who were being nursed on the Balmoral pressure mattress who had existing pressure ulcers.
• One resident had developed a category 2 pressure ulcer to their elbow, but the care home staff believed that this had developed due to the resident leaning on the chair and was therefore not associated with use of the mattress.
• Another resident had 2 category 2 pressure ulcers to their heels, but these had developed due to direct contact between the resident’s heels and a specialist chair footplate, so again this was not deemed to be associated with use of the Harvest Balmoral mattress.
• A further 6 residents with pressure ulcers; Category II (1 resident); Category III (2 residents) and Category IV (2 residents) had been admitted to the care home with pressure ulcers and were being nursed on the Harvest Balmoral mattress as part of a package of care to prevent further pressure ulcers and to expedite healing of these existing pressure ulcers. In all of these cases, the resident’s wounds were showing signs of ongoing improvement.
• Those with a history of pressure ulceration (3 residents) but were now ulcer free had healed whilst using the Balmoral mattress and had remained healed and ulcer free during their time using the mattress
3.0 Summary
Post-market clinical follow-up on the Harvest Balmoral Alternating Mattress was undertaken between August and December 2022 using an independent clinical advisor to undertake the audit and collate the data. A Total of 12 Independent Care Homes which used Harvest pressure-reducing mattresses were visited by the Independent Clinical Advisor (11 of these Care Homes had a total of 82 residents who were using the Balmoral alternating mattress) and a review of equipment in use within the care home was undertaken at each site. Whilst on site the Independent Nurse Advisor was provided with anonymised information for each of the residents to enable the collation of real-world PMCF performance data for the Harvest Balmoral Mattress.
Data collected so far suggests that the Harvest Balmoral Mattress performs well for prevention of pressure ulcers in the 24-hour care home provider environment for elderly residents (where regular repositioning and continuous support via carers is available), with low, medium or high weights, those who are at very high risk of pressure ulceration and those with comorbidities such as Diabetes, CVA and Dementia or Cognitive impairment.
It also suggests that the mattress performs well for those with pressure ulcers of Category II, III or IV and can also be used for those with a history of previous pressure ulceration to prevent further ulceration, although the numbers of residents where this was observed during the audit was small (n=3).
Harvest Healthcare aims to continue to collect this PMCF data via collaborative working with care home providers to increase the number of residents audited and to provide robust post-market clinical follow-up data.
Report compiled by:
N Morton
Independent Nurse Advisor / Educator
RGN, BSc Hons Nursing, MSc Wound Healing and Tissue Repair, PG Cert HE
04/01/2023
For more information about Harvest Healthcare please click here
For more news please visit our Twitter
Or follow us on LinkedIn