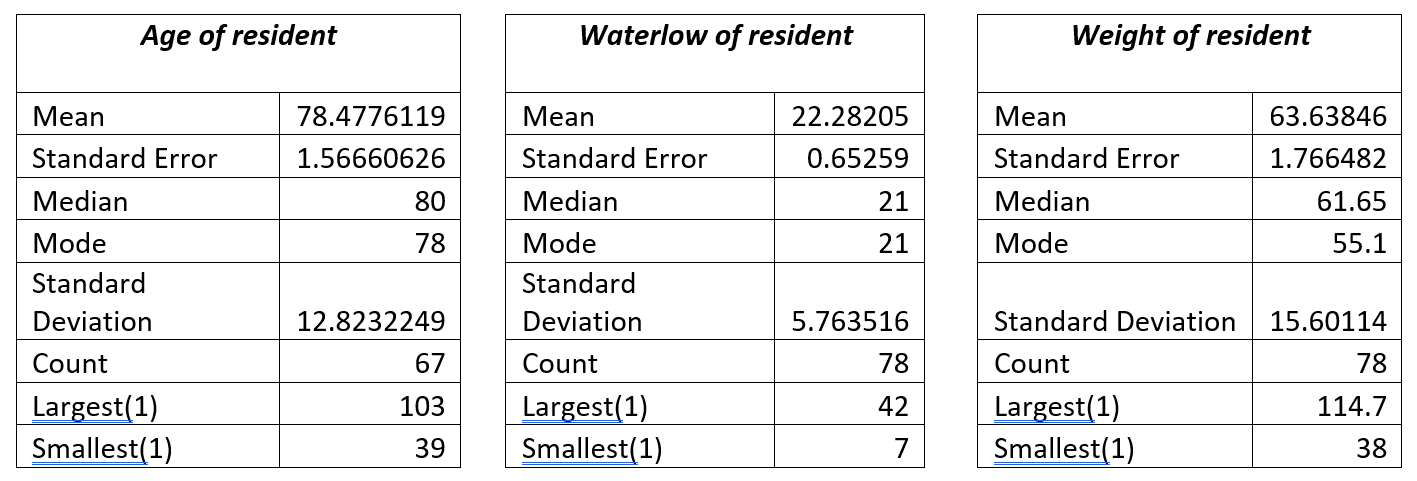
In 2016, around 13% of adults worldwide were affected by obesity, as defined by the World Health Organization (WHO, 2021), characterising an abnormal excess of body fat posing health risks. Epidemiological studies indicate a steady rise in obesity prevalence in recent decades, reaching epidemic levels (Großschädl & Stronegger, 2019; NCD-RisC, 2017), with projections indicating a continued increase (Thomas et al., 2014).
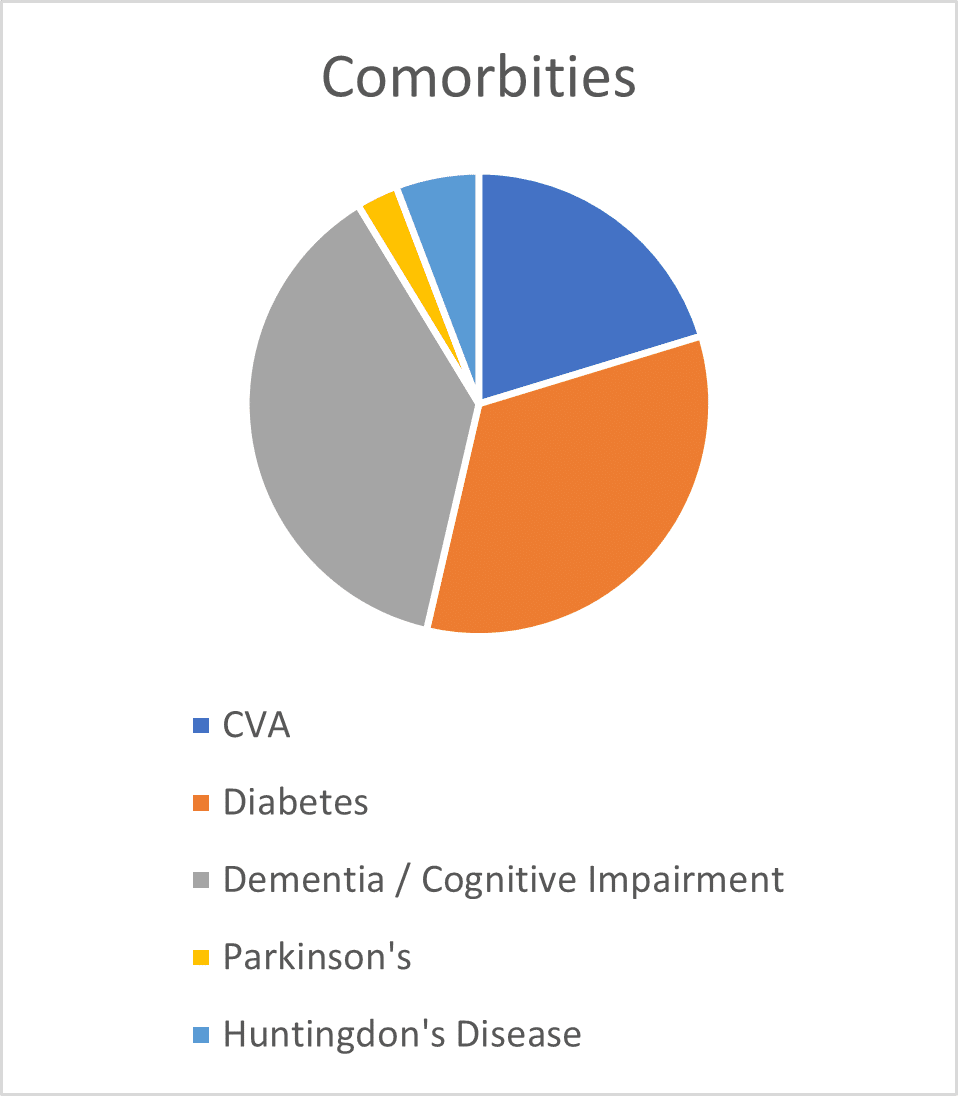
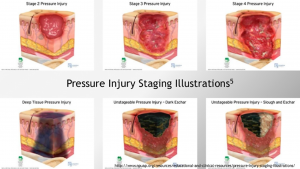
The prevalence of obesity among residents in nursing homes is also on the rise, potentially impacting required nursing care, facility provisions, and morbidity rates. A US study revealed a significant increase in obesity prevalence among newly admitted nursing home residents, rising from 16.9% to 25.8% over ten years (Cai, Rahman et al., 2013). Additionally, residents with moderate or severe obesity had a 15.0% higher likelihood of developing pressure ulcers compared to non-obese residents in the same facility, highlighting associated health risks.
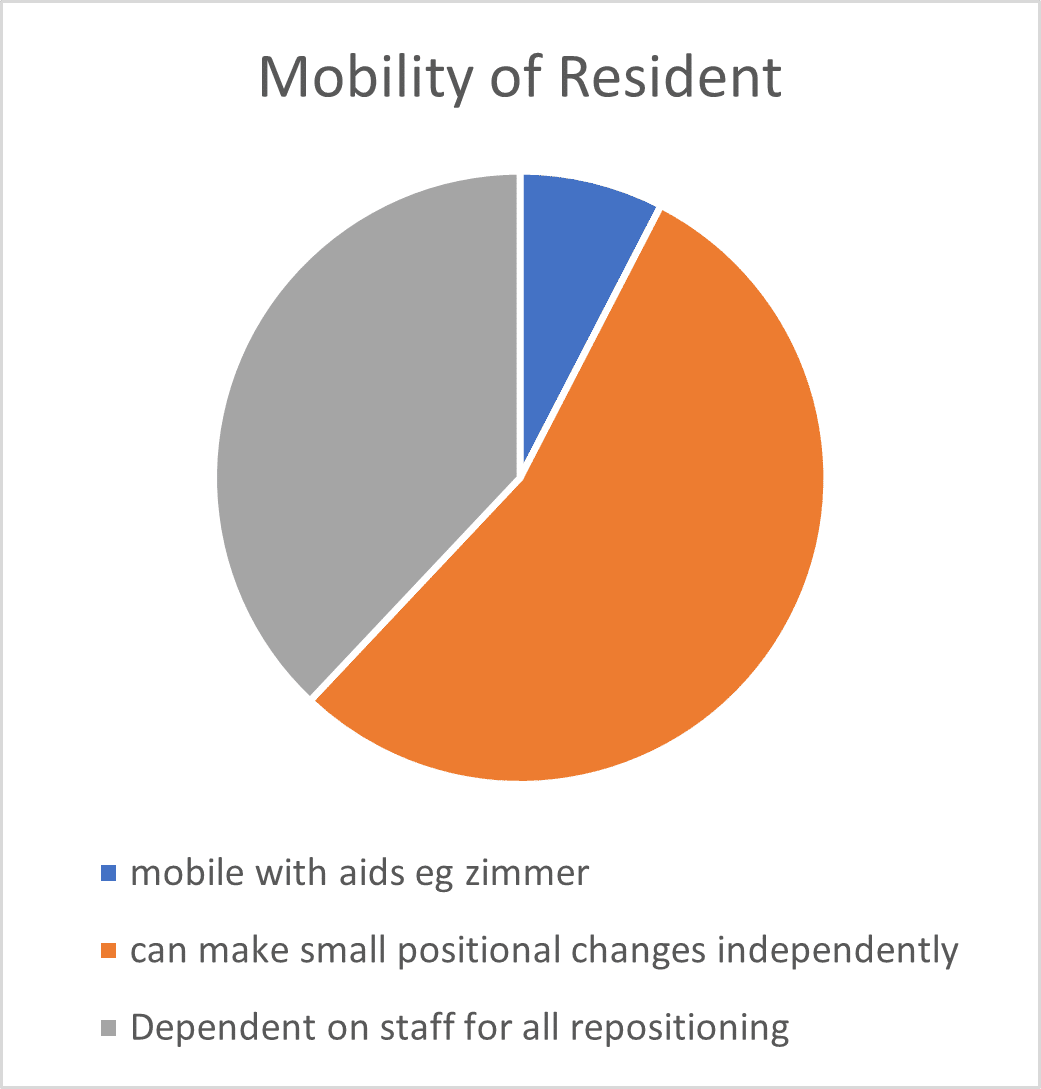
Increased body mass often leads to reduced mobility, complicating care tasks such as repositioning and increasing the risk of secondary health issues, all contributing to pressure ulcer development risk factors.
Ensuring accessible care for all is paramount, particularly in private and non-purpose-built nursing homes. Considering these statistics, it’s evident that plus-sized patients require specialised care with the appropriate equipment. However, this presents its own challenges for both care homes and community equipment providers.
Sourcing the required equipment can be challenging. This leads to many care providers lacking the necessary equipment to support bariatric individuals, especially in larger quantities. This impacts timely care delivery, care home admissions, and patient discharge from hospitals.
Residences may also face infrastructure limitations hindering care for plus sized individuals further complicating care provision. Acute care environments recommend spacious rooms for plus sized patients, posing a further challenge for many long-term care settings (Muir, 2009).
At Prism Healthcare Group, we are dedicated to easing the burden of sourcing and fitting bariatric equipment, allowing caregivers to concentrate on delivering high-quality care. Our Prism Plus line features an extensive range of bariatric products designed to streamline selection, backed by knowledgeable customer service and sales teams ready to address any challenges.
Our products are designed to enhance the quality of life for residents and caregivers, ensuring equitable access to care and support.
For more information on Prism Plus products, please visit the Prism Healthcare website.
References
Großschädl, F., Schoberer, D., Eglseer, D., Lohrmann, C., Everink, I., Gordon, A. L., Schols, J. M. G. A., & Bauer, S. (2023). Obesity and its associated factors in older nursing home residents in three European countries—Secondary data analyses from the “International Prevalence Measurement of Care Quality”. International Journal of Older People Nursing, 18, e12530.
Cai, S., M. Rahman and O. Intrator (2013). “Obesity and pressure ulcers among nursing home residents.” Medical care 51(6): 478-486.
Muir, M. (2009) “Space Planning for the Bariatric Patient.” Bariatric Times.
For more information please visit the Harvest Healthcare website
For news and updates please follow our LinkedIn page
Or browse our Twitter feed